The PCOS Belly: Causes, Solutions, and Body Image
Introduction

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder that affects individuals in various ways. Among the common concerns associated with PCOS is the development of what is colloquially referred to as the “PCOS belly.” In this article, we will delve into the causes of the PCOS belly, explore solutions to manage it, and discuss the impact of body image in the context of this condition.
Understanding PCOS
The Basics of PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects individuals with ovaries. It is characterized by various symptoms and hormonal imbalances, including irregular menstrual cycles, excessive androgen (male hormone) levels, and the presence of small cysts on the ovaries. PCOS can lead to a range of health issues, including fertility challenges, insulin resistance, weight gain, and skin problems. Effective management often involves lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and a holistic approach to address its complex nature. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment can help individuals with PCOS lead healthier lives.
PCOS and Hormonal Imbalance
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is characterized by a significant hormonal imbalance in individuals with ovaries. This hormonal disruption plays a central role in the development of PCOS and its associated symptoms. Key hormonal factors involved in PCOS include:
- Insulin Resistance: Many individuals with PCOS exhibit insulin resistance, a condition where cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This leads to elevated insulin levels, which can trigger the ovaries to produce excess androgens (male hormones).
- Androgens (Male Hormones): Elevated androgen levels, including testosterone, are common in PCOS. This hormonal excess can result in symptoms such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): LH levels are often higher than normal in PCOS. This can disrupt the regular menstrual cycle and lead to irregular periods or anovulation (lack of ovulation).
- Estrogen and Progesterone: Imbalances in estrogen and progesterone levels can result in irregular menstrual cycles, amenorrhea (absence of menstruation), and other reproductive health issues.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): In some cases, FSH levels may be lower than LH levels, further contributing to irregular ovulation and menstrual disturbances.
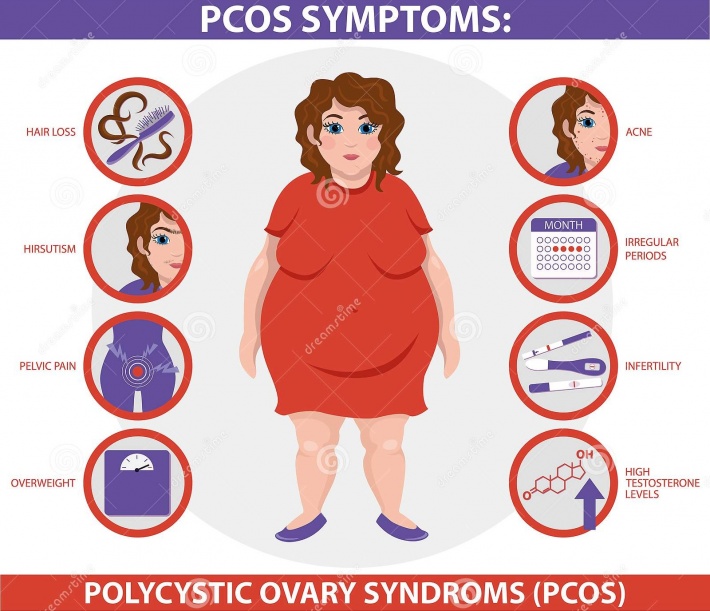
This intricate web of hormonal imbalances can lead to various PCOS symptoms, including infertility, weight gain, mood swings, and skin problems. Addressing these hormonal disruptions is a key component of PCOS management. Treatments may include lifestyle changes, medications to improve insulin sensitivity, and hormonal contraceptives to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels. Balancing hormones is essential for improving the overall health and well-being of individuals with PCOS.
Causes of the PCOS Belly

The development of the “PCOS belly,” often characterized by abdominal weight gain, is a common concern for individuals with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Several factors contribute to this phenomenon:
- Chronic Inflammation: PCOS is also linked to chronic inflammation in the body. Inflammatory processes can contribute to abdominal fat deposition and insulin resistance, further exacerbating the PCOS belly.
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors may play a role in determining how and where fat is stored in the body. Some individuals with PCOS may have a genetic predisposition to store fat in the abdominal region.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: Sedentary behavior and poor dietary choices can contribute to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen. Lifestyle factors can worsen insulin resistance and exacerbate the PCOS belly.
Solutions for Managing the PCOS Belly
Managing PCOS at home involves making lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being. While PCOS is a complex medical condition that may require medical intervention in severe cases, the following home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can help:
-
Dietary Changes:

- Balanced Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Low Glycemic Index (GI) Foods: Choose foods with a low GI to help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit processed and sugary foods, as they can exacerbate insulin resistance and weight gain.
-
Regular Exercise:

- Engage in regular physical activity to help manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce abdominal fat.
- Incorporate both aerobic exercises (e.g., brisk walking, swimming) and strength training into your routine.
-
Stress Management:

- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or mindfulness to lower cortisol levels, which can affect hormonal balance.
-
Adequate Sleep:

- Ensure you get enough quality sleep each night, as sleep disturbances can worsen PCOS symptoms and insulin resistance.
-
Weight Management:

- If overweight, aim for gradual and sustainable weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise.
- Even modest weight loss can improve hormonal balance and reduce PCOS symptoms.
-
Natural Supplements:
- Some individuals find relief from PCOS symptoms by taking supplements like inositol, chromium, or cinnamon, but consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.
-
Limiting Caffeine and Alcohol:

- Reduce caffeine and alcohol intake, as they can disrupt hormonal balance and affect insulin sensitivity.
-
Stay Hydrated:

- Drink plenty of water to support overall health and help manage weight.
-
Regular Monitoring:

- Keep track of your menstrual cycles, symptoms, and any changes in weight or mood. This information can be valuable when consulting a healthcare provider.
-
Consult a Healthcare Professional:

- While home remedies can be beneficial, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan.
- Medical treatments such as birth control pills, insulin-sensitizing medications, or fertility treatments may be recommended depending on your specific needs.
Remember that PCOS varies from person to person, and what works for one individual may not work the same way for another. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can tailor a treatment plan to your unique situation. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing PCOS at home is a long-term commitment, so consistency is key to seeing positive changes over time.
Medical Interventions
Certainly, medical interventions for PCOS are approaches that involve the use of medications or medical procedures to manage the condition. PCOS is a hormonal disorder, and medical interventions aim to address the underlying hormonal imbalances and alleviate the associated symptoms. Here’s a more detailed explanation of medical interventions for PCOS:
-
Birth Control Pills (Oral Contraceptives):
- Birth control pills are often prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle in individuals with irregular periods caused by PCOS.
- They contain hormones (estrogen and progestin) that help regulate hormone levels, reduce androgen production, and promote regular menstruation.
- Birth control pills can also help control acne and reduce the risk of endometrial cancer associated with PCOS.
- read more about Birth Control Method”
-
Anti-Androgen Medications:

- Some individuals with PCOS experience excessive hair growth (hirsutism) and acne due to elevated androgen levels. Anti-androgen medications like spironolactone may be prescribed to reduce these symptoms.
- Spironolactone blocks the effects of androgens and can help improve skin complexion and reduce excess body hair.
-
Insulin-Sensitizing Medications:

- Insulin resistance is a common feature of PCOS, leading to elevated insulin levels. Medications like metformin may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Metformin helps lower insulin levels, which, in turn, can lead to improved ovarian function, more regular menstrual cycles, and reduced androgen levels.
- It may also assist with weight management in some individuals.
-
Fertility Medications:
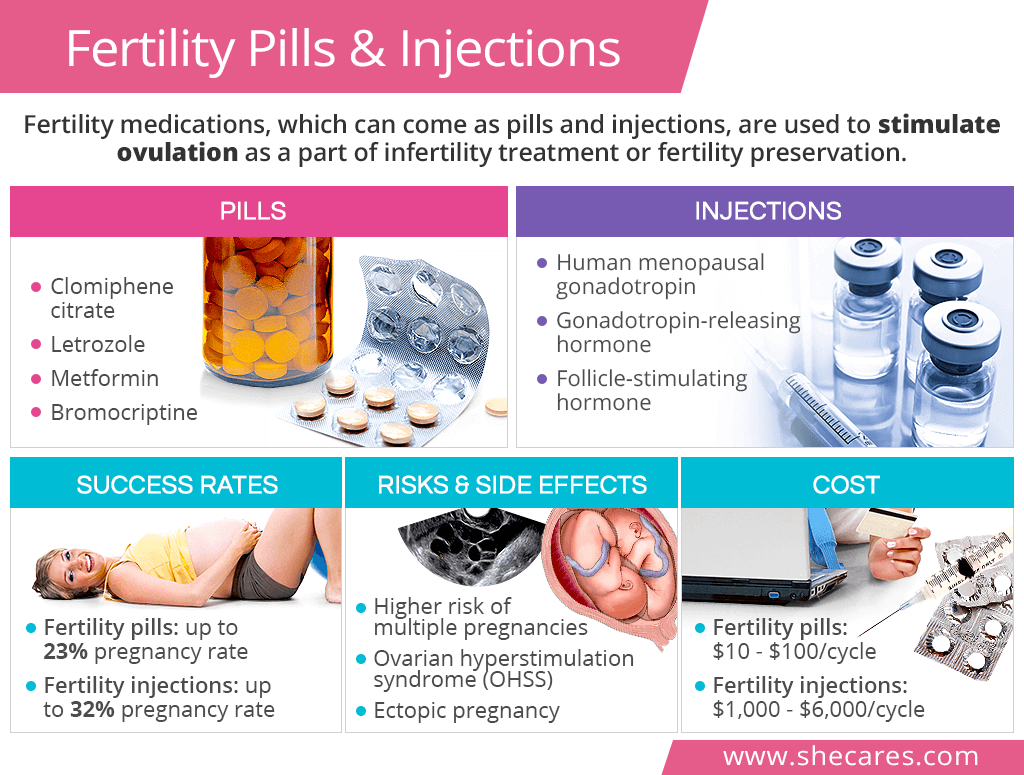
- For individuals with PCOS who are trying to conceive, fertility medications such as clomiphene citrate (Clomid) may be prescribed.
- These medications stimulate ovulation and increase the chances of getting pregnant.
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
- While not strictly medical interventions, healthcare providers often emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise, as part of the overall treatment plan.
- Lifestyle changes can complement medical interventions by promoting weight loss, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing symptoms.
-
Ovarian Drilling (Laparoscopic Ovarian Diathermy):

- In cases where other treatments have not been effective, a surgical procedure called ovarian drilling may be considered.
- This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions in the ovaries and using heat or laser to destroy a portion of ovarian tissue.
- Ovarian drilling can help induce ovulation in some individuals with PCOS.
It’s important to note that the choice of medical intervention depends on individual factors, such as the specific symptoms and goals of the person with PCOS. Healthcare providers will conduct a thorough evaluation, including hormone testing and medical history, to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Medical interventions can be highly effective in managing PCOS and improving quality of life. However, it’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor progress and adjust treatments as needed to achieve the best possible outcomes.
The Emotional Aspect: PCOS and Body Image
The Mental Health Connection
The physical manifestations of PCOS, including the PCOS belly, can impact mental health and self-esteem. We’ll address the emotional challenges many individuals face.
Body Positivity and Self-Care
Navigating body image concerns is an essential aspect of PCOS management. Explore strategies for fostering body positivity and practicing self-care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the PCOS belly is a common concern for individuals with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. However, understanding its causes and implementing effective solutions can help manage this aspect of PCOS. Furthermore, addressing the emotional impact of PCOS on body image is crucial for holistic well-being.
FAQs
Q1: What is PCOS, and how common is it among individuals?
Q2: How does insulin resistance contribute to the PCOS belly, and can it be managed?
Q3: What role do androgen hormones play in weight gain associated with PCOS?
Q4: Are there specific diets recommended for managing PCOS and reducing abdominal fat?
Q5: How can individuals with PCOS improve their body image and self-esteem?
In this article, we’ve explored the intricacies of the PCOS belly, from its underlying causes to practical solutions and the emotional aspects surrounding body image. Whether you’re seeking ways to manage your PCOS or aiming to support someone with this condition, this comprehensive guide offers valuable insights.









 Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
