Rare Blood Diseases: Unmasking the Hidden Challenges
Introduction
Blood diseases come in various forms, with some being well-known and others lurking in the shadows of obscurity. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intriguing world of rare blood diseases. From their causes to symptoms, diagnosis to treatment options, we’ll uncover the mysteries surrounding these conditions. So, whether you’re a patient seeking information or just curious about the unusual, this article is your go-to resource.
Understanding Rare Blood Diseases
Rare blood diseases, also known as orphan diseases, are medical conditions that affect a very small portion of the population. They often go unnoticed in the grand scheme of healthcare due to their low prevalence. While the exact number of rare blood diseases is difficult to pin down, there are over 7,000 recognized rare diseases, and a significant portion of them affect the blood.
Common Rare Blood Diseases
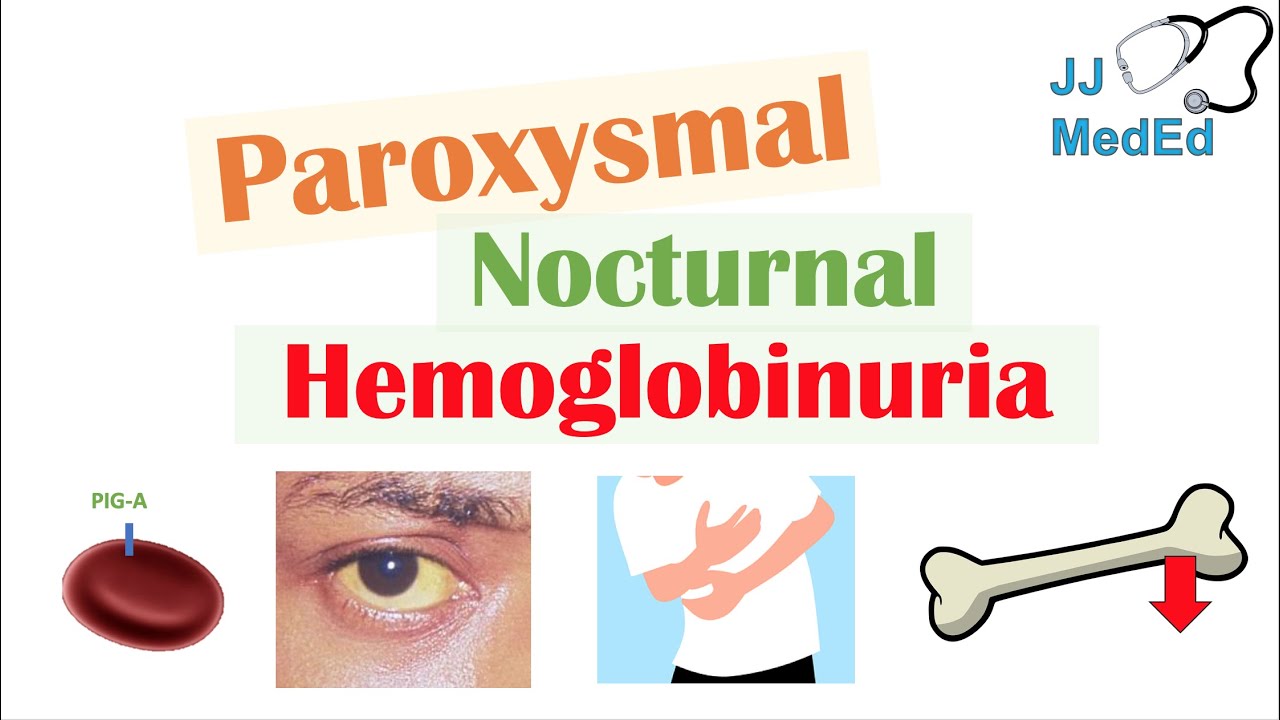
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH): One of the rarest blood diseases, PNH causes the destruction of red blood cells and leads to anemia, blood clots, and other complications.
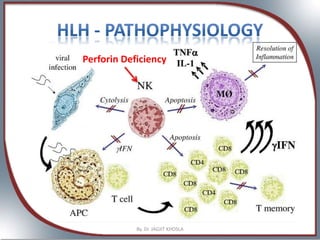
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH): HLH is a rare immune disorder that causes an overproduction of white blood cells, leading to fever, organ failure, and life-threatening complications.
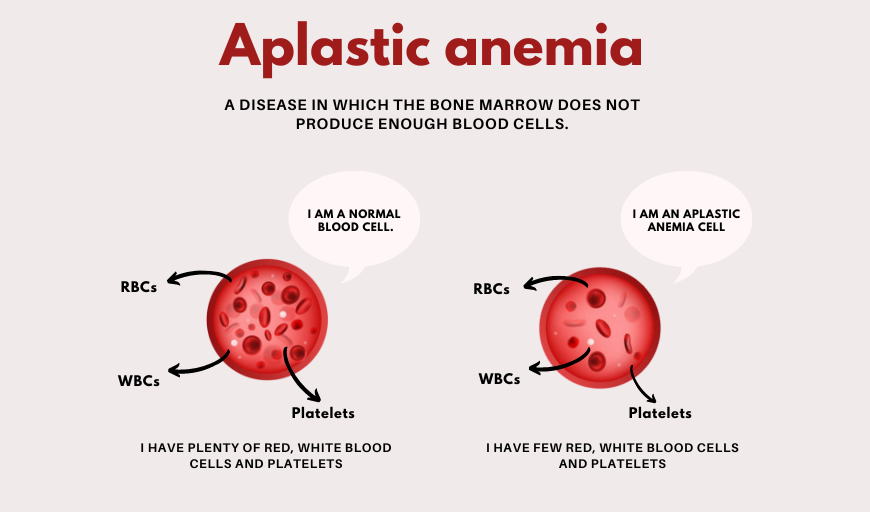
- Aplastic Anemia: This rare condition results in bone marrow failure, causing a reduction in red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the root causes of rare blood diseases is often a complex puzzle. Some of these diseases have a genetic basis, while others are acquired due to environmental factors. Risk factors can vary, but here are a few common ones:
- Genetic Mutations: Many rare blood diseases are inherited, stemming from specific gene mutations passed down through families. Understanding one’s family medical history is essential in identifying such conditions.
- Autoimmune Reactions: Some rare blood diseases, like PNH, result from the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy blood cells.
- Exposure to Toxins: Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, or infections, can trigger rare blood diseases like aplastic anemia.
Symptoms of Rare Blood Diseases

Rare blood diseases often manifest in various ways, and symptoms can be subtle or severe. Early detection and proper diagnosis are crucial to managing these conditions effectively. Common symptoms may include:
- Fatigue: Many rare blood diseases lead to anemia, resulting in persistent fatigue and weakness.
- Easy Bruising and Bleeding: Decreased platelet count can cause excessive bruising and prolonged bleeding.
- Enlarged Spleen: An enlarged spleen can occur in conditions like PNH and HLH, leading to abdominal discomfort.
- Frequent Infections: Some rare blood diseases compromise the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Pain: Patients may experience bone pain due to an inadequate supply of blood to the bones.
Diagnosis and Testing

Given their rarity, diagnosing these conditions can be challenging. However, advancements in medical technology have improved diagnostic accuracy. Some of the common diagnostic methods include:
- Blood Tests: Comprehensive blood tests can reveal abnormalities in blood cell counts and functions, aiding in identifying the specific rare blood disease.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: A bone marrow biopsy is often necessary to assess the bone marrow’s health and functionality.
- Genetic Testing: For conditions with a known genetic component, genetic testing can provide valuable insights.
Treatment Options

Managing rare blood diseases usually involves a combination of medical interventions. Here are some common treatment options:
- Blood Transfusions: Patients with anemia may require regular blood transfusions to maintain adequate hemoglobin levels.
- Medications: Immunosuppressive drugs, steroids, or medications targeting specific aspects of the disease can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: For some patients, a bone marrow transplant can ofxe fer a potential cure.
- Supportive Care: Addressing specific symptoms and complications, such as infection control or pain management, is essential in improving the patient’s quality of life.
The Importance of Raising Awareness
Raising awareness about rare blood diseases is critical. Due to their low prevalence, research and funding are often limited. By increasing public knowledge and advocating for these conditions, we can promote research and improve the lives of those affected.
Transitioning to Hope: Promising Research
While living with a rare blood disease can be challenging, there is hope on the horizon. Researchers are continually exploring innovative treatments and therapies. For example:
- Gene Therapies: Cutting-edge gene therapies show promise in addressing genetic mutations that cause certain rare blood diseases.

- Stem Cell Research: Ongoing research into stem cell therapy may offer new treatment options for patients with aplastic anemia and related conditions.

Read more about Stem Cell Research Therapies and Technologies
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide patients with access to novel treatments and contribute to the advancement of medical science.
Conclusion
Rare blood diseases, though obscure, have a significant impact on those who suffer from them. Understanding these conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for both patients and the broader medical community. By raising awareness, supporting research, and advocating for better resources, we can shine a light on these rare blood diseases and help those affected lead healthier and more fulfilling lives. So, let’s unite in our quest for knowledge and a brighter future for those facing the challenges of rare blood diseases.
FAQs
Frequently asked questions about rare blood diseases
- What makes a blood disease “rare”? Rare blood diseases are classified as such due to their low prevalence in the general population.
- Are rare blood diseases treatable? Yes, many rare blood diseases are treatable, but the approach varies depending on the specific condition and its severity.
- Can rare blood diseases be prevented through genetic testing? In some cases, genetic testing can help identify individuals at risk for rare blood diseases, but prevention may not always be possible.
- How can I support research on rare blood diseases? You can support research by participating in clinical trials, donating to organizations focused on rare diseases, and raising awareness.
- Is there hope for finding a cure for rare blood diseases? Research into rare blood diseases is ongoing, and with advancements in medical science, there is hope for finding more effective treatments and even cures in the future.





 Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
