The Evolution of Biotechnology: Bridging Biology and Technology
Unveiling the Power to Recode Life
In the dynamic intersection of biology and technology, a transformative power emerges—the ability to recode life itself. Human ingenuity is rapidly advancing, from organ farms and artificial wombs to robots boasting biological components. This article explores the profound implications of this burgeoning field, delving into the extraordinary world of biotechnology.

The Bioengineering Frontier: Unleashing Genetically Altered Humans
As the boundaries between biology and technology blur, a new era dawns—one where genetically altered humans possess the ability to heal through touch and much more. However, as we venture into this brave new world, questions arise about the environmental impact and the potential consequences of engineering life.

Bioprinting: Breathing Life into Objects
At the forefront of biotechnology lies bioprinting, a revolutionary process that goes beyond traditional 3D printing. Instead of using plastic or metal, living cells called bioinks are utilized to print biological structures layer by layer. This technique breathes life into various applications, ranging from bioprinted organs to advanced corneas and hair follicles.

The Future Landscape: Bioprinted Coral Reefs and Robotic Space Stations
Looking ahead, bioprinting holds promise for crafting 3D printed coral reefs that restore damaged ecosystems and small-scale robotic space stations functioning as bioprinting factories. These innovations signify a paradigm shift in our relationship with nature, with humans evolving from observers to masters.

Living Architecture: Buildings with a Biological Twist
The integration of bioengineered materials in construction has given rise to living architecture. These buildings self-repair, clean the air, absorb pollutants, and even reproduce. Furthermore, gecko-inspired adhesives and coral reef-inspired eco-concrete contribute to sustainable construction practices.

Illuminating the Night: Bioluminescent Lights Replace Streetlights
In city bio apartments, near the ocean, living sea walls made from genetically engineered corals and muscles protect against rising sea levels. The streets are lit by bioluminescent lights—plants, bacteria, and algae engineered to glow in the dark, mimicking deep-sea creatures and replacing traditional electric streetlights.
Beneath the Surface: The World of Underground Biohackers
Hidden from regulatory oversight, biohackers in underground labs experiment with implanting microchips, tattooing with digital inks, and even creating biocomputers from living neural tissue. Cryonic punks freeze themselves in hopes of future revival, while chimeras—animals with genes from multiple species—spark controversy.
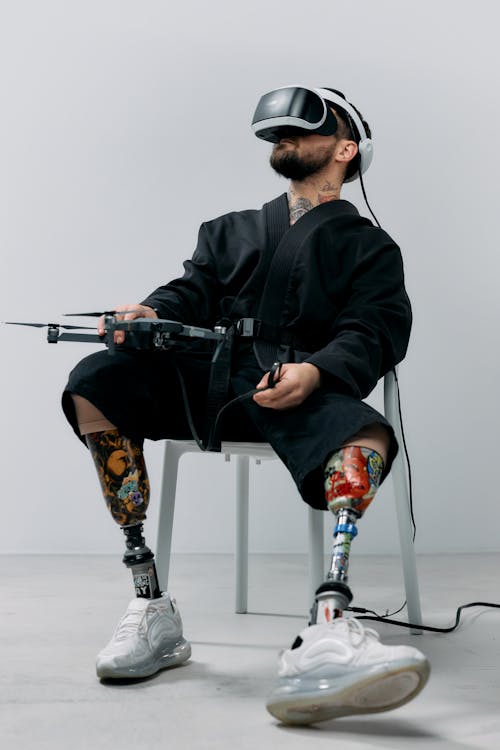
Bionic Prosthetics: From Ownership Debates to Seamless Integration
The evolution of bionic prosthetics raises questions about ownership, with corporations rendering older models obsolete. Fully integrated bioprinted prosthetic limbs, seamlessly connected to the nervous system, offer users a sense of touch and natural control. Governments employ bionic limbs for creating super soldiers, pushing the boundaries of human enhancement.

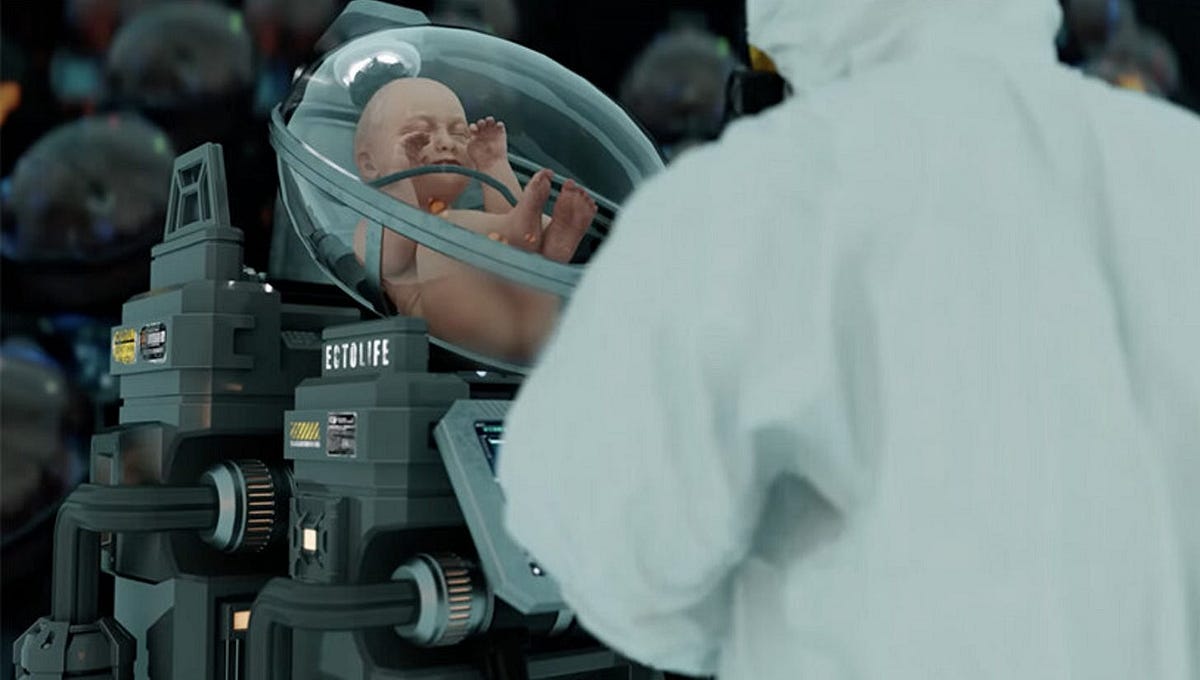
Artificial Wombs and Extended Gestation: Redefining Childbirth
In controlled labs, scientists explore advanced artificial womb technology, including ectogenesis for external pregnancy and gestation. Artificial wombs address infertility concerns, with wealthy individuals outsourcing childbirth to large womb farms. Conspiracy theories abound, speculating on dictators creating immortal legacies through artificial wombs.
Bio-Hybrid Robots: The Future of Robotics
Enter the era of bio-hybrid robots, seamlessly blending biological tissue for enhanced flexibility and energy efficiency. Corporations develop biomimetic robots for environmental monitoring and research, but concerns arise about unintentional ecological disruption and potential espionage applications.

A Restorer of Extinct Species: Bio-Hybrid Robots with a Noble Cause
Bio-hybrid robots emerge as saviors in the aftermath of nuclear-scale biowaste catastrophes. Immune to radiation, they scavenge resources, rescue survivors, and restore extinct animals. These neo-humans, representing a new species, push the boundaries of what it means to be human.

The Neo-Humans: A Glimpse into Humanity’s Future
The advent of bioengineered humans, dubbed neo-humans, brings forth individuals with extraordinary abilities. From living musical instruments to human insect repellents and age-reversal experiments, these pioneers redefine the boundaries of human potential.
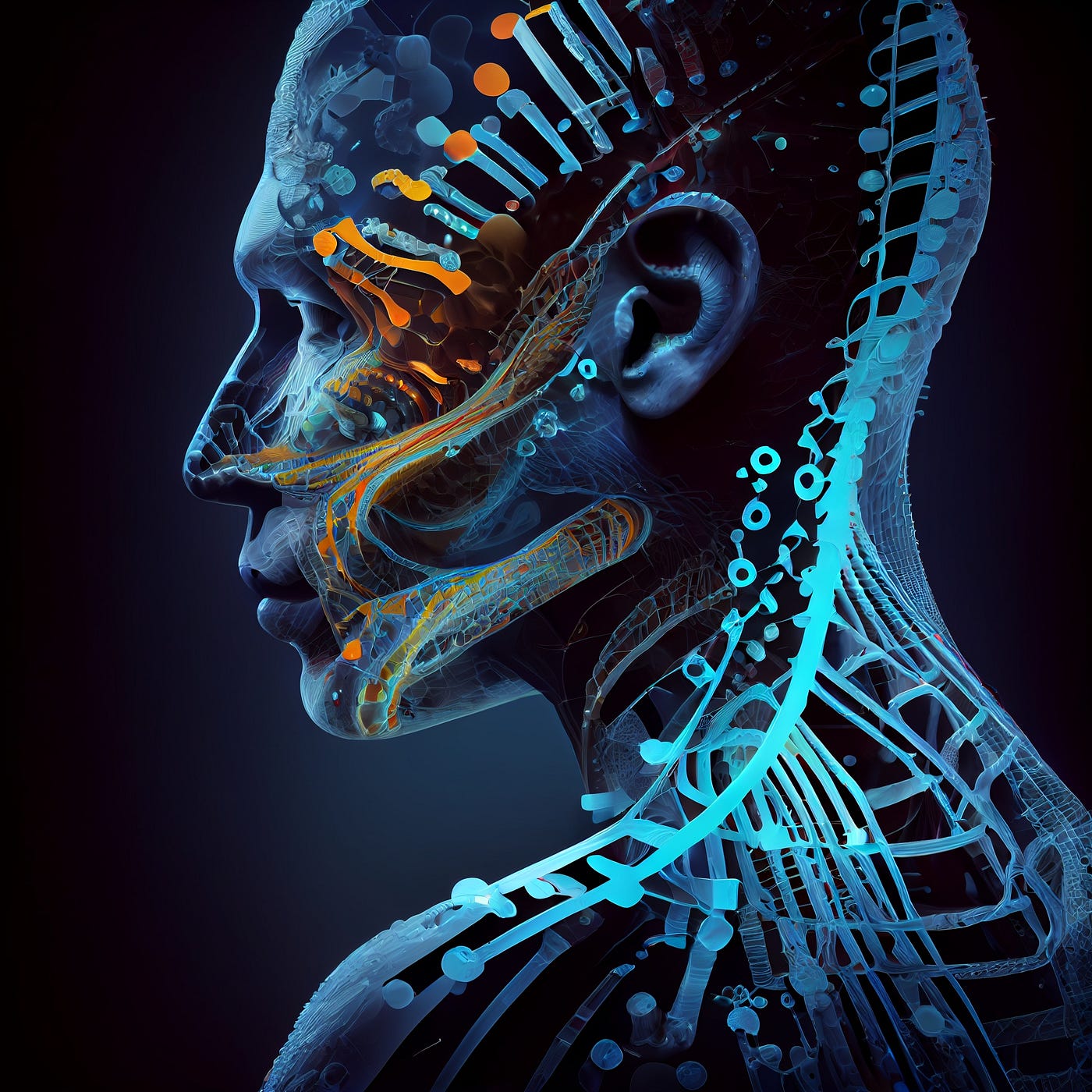

Multifaceted Capabilities: Splitting Consciousness and Healing through Touch
Neo-humans claim diverse capabilities, including splitting consciousness through organic brain augmentations and healing others through regenerative cell transfer. Biotechnology becomes the canvas where nature’s blueprint converges with human design, propelling humanity into the next phase of evolution.
In conclusion, the fusion of biology and technology through biotechnology heralds a transformative chapter in human history. As we navigate this uncharted territory, the ethical implications and societal consequences must be carefully considered to ensure a responsible and sustainable evolution for humanity.
Conclusion
The intertwining of biology and technology, manifested through the field of biotechnology, unveils a remarkable journey into the future of human evolution. From bioprinting organs to the emergence of neo-humans with extraordinary capabilities, our world is on the cusp of transformative changes. As we embrace the potential benefits of biotechnology, we must also navigate the ethical challenges and environmental considerations that come with playing the role of masters rather than mere observers of nature. The fusion of living organisms with technological advancements holds both promises and perils, urging us to tread carefully as we embark on this unprecedented phase in humanity’s evolution.
FAQs:
Q1: What is bioprinting, and how does it differ from traditional 3D printing? A1: Bioprinting is a cutting-edge technique that utilizes living cells, known as bioinks, to create biological structures layer by layer. Unlike traditional 3D printing, which uses plastic or metal, bioprinting breathes life into objects, offering applications ranging from organ manufacturing to coral reef restoration.
Q2: How are artificial wombs changing the landscape of childbirth? A2: Artificial wombs, a product of advanced biotechnology, are redefining childbirth by enabling more reliable external pregnancy and gestation in controlled pod devices. This technology addresses infertility concerns and sparks debates about its potential uses, from outsourcing childbirth to wealthy individuals to conspiracy theories surrounding dictatorial legacies.
Q3: What are the ethical implications of bio-hybrid robots? A3: Bio-hybrid robots, integrating biological tissue with technology, present ethical concerns related to unintentional ecological disruptions and potential espionage applications. As these robots become restorers of extinct species and immune to radiation, careful consideration of their impact on ecosystems and global security is essential.
Q4: Who are neo-humans, and what extraordinary capabilities do they possess? A4: Neo-humans represent a new breed of individuals created through bioengineering. They showcase diverse capabilities, from living musical instruments to human insect repellents and age-reversal experiments. As pioneers in redefining human potential, neo-humans raise intriguing questions about the boundaries of our abilities.
Q5: How does biotechnology address environmental challenges? A5: Biotechnology offers innovative solutions to environmental challenges, including living architecture that self-repairs and cleans the air, bioluminescent lights replacing traditional streetlights, and bio-hybrid robots restoring ecosystems after biowaste catastrophes. However, concerns about potential misuse and forced obsolescence must be addressed.
In navigating the biotechnological frontier, society must engage in thoughtful dialogue, ethical considerations, and responsible innovation to ensure a harmonious integration of biology and technology. The journey ahead holds immense potential for progress, but the path must be charted with a careful balance between innovation and ethical responsibility.





 Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine

66 Comments