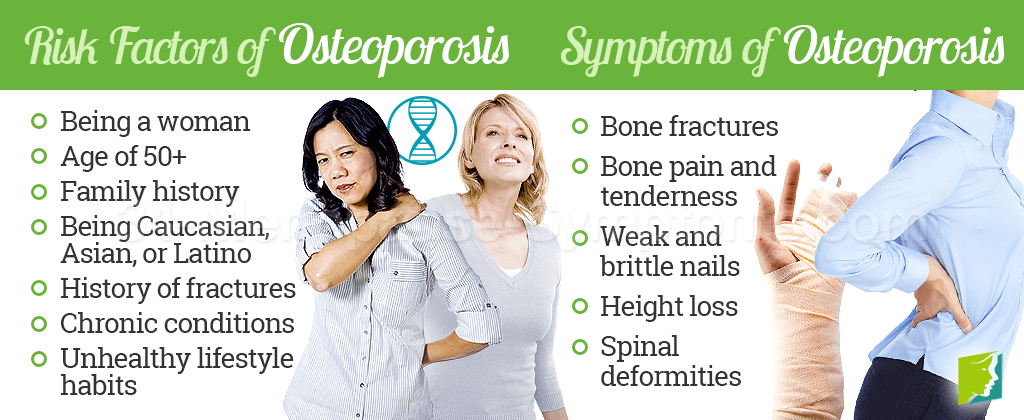
7 Risk Factors for Osteoporosis: Protecting Your Bones
Introduction
Osteoporosis, often referred to as the “silent disease,” is a condition that weakens the bones, making them fragile and more prone to fractures. This debilitating ailment affects millions of people worldwide, especially postmenopausal women and the elderly. Understanding the risk factors associated with osteoporosis is crucial for prevention and early intervention. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the seven key risk factors for osteoporosis, providing valuable insights and practical advice to safeguard your bone health.
read more about Bone and Tooth Health Essentials: Tips for Strong and Healthy Skeletal System
What is Osteoporosis?
Before we delve into the risk factors, let’s briefly understand what osteoporosis is. Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by a loss of bone density and quality, leading to weakened and brittle bones. This increased fragility elevates the risk of fractures, even with minimal trauma. It’s often asymptomatic until a fracture occurs, making early detection and prevention vital.

The Age Factor
One of the most significant risk factors for osteoporosis is age. As we grow older, our bone density naturally decreases. This decline typically begins in our mid-30s and accelerates after menopause in women. The older we get, the more vulnerable our bones become.

Menopause and Osteoporosis
In women, the hormonal changes associated with menopause can lead to a rapid reduction in bone density. Estrogen, a hormone that plays a critical role in bone health, decreases during menopause, accelerating bone loss.
Gender and Genetics
Gender and genetics also play a pivotal role in the risk of developing osteoporosis. Women are more likely to suffer from this condition than men, mainly due to hormonal differences. Moreover, a family history of osteoporosis increases your susceptibility.
Are You at Risk Due to Genetics?
If your parents or grandparents have a history of osteoporosis or fractures, you should be particularly cautious. Genetics can predispose you to lower bone density and, consequently, a higher risk of osteoporosis.
Lifestyle Choices
Certain lifestyle choices can significantly impact your bone health. Factors such as diet, physical activity, and smoking can increase your risk of developing osteoporosis.
The Importance of a Calcium-Rich Diet

A diet low in calcium can weaken your bones, as this mineral is essential for bone strength. Ensuring you consume adequate dairy products and leafy greens is crucial in preventing osteoporosis.
The Role of Exercise

Sedentary lifestyles are detrimental to bone health. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and strength training, help maintain bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones. If you’re a smoker or consume alcohol in excess, you’re at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis.
Medications and Medical Conditions

Certain medications and underlying medical conditions can contribute to osteoporosis.
Medications to Watch Out For
Long-term use of corticosteroids, often prescribed for conditions like asthma and arthritis, can decrease bone density. If you’re on these medications, discuss bone health with your healthcare provider.
Conditions That Impact Bone Health
Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease can interfere with your body’s ability to absorb nutrients critical for bone health.
Body Size and Composition
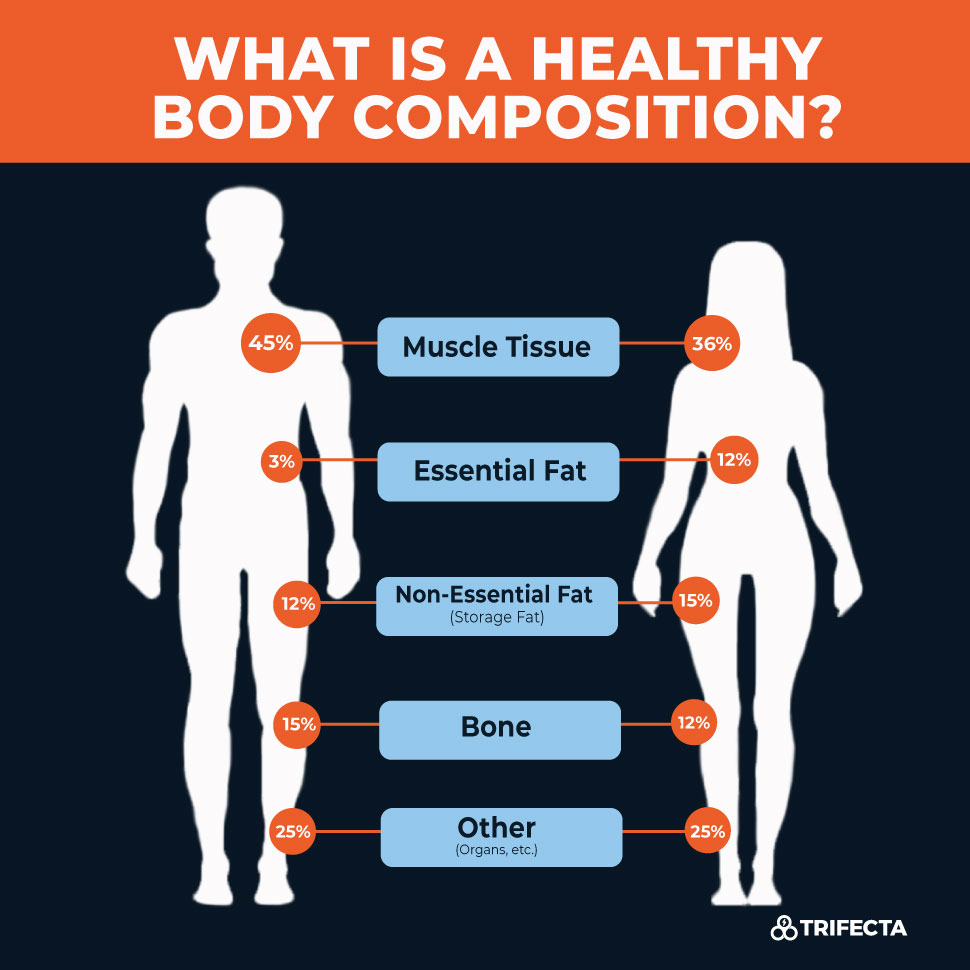
Your body size and composition can also affect your risk of osteoporosis. People with a small, thin frame are at a higher risk because they typically have less bone mass to start with.
The Dangers of Being Underweight
Being significantly underweight can increase your risk of developing osteoporosis. Adequate nutrition and maintaining a healthy body weight are essential for bone health.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances, aside from those related to menopause, can also contribute to osteoporosis.
Thyroid Problems
An overactive or underactive thyroid can disrupt the balance of calcium and hormones in the body, potentially leading to bone loss.
Prevention and Conclusion
Preventing osteoporosis involves making healthy lifestyle choices, staying physically active, maintaining a well-balanced diet, and regular check-ups with your healthcare provider. Understanding the risk factors and taking proactive measures can help you protect your bones and enjoy a life free from the limitations of osteoporosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the best age to start taking preventive measures against osteoporosis?
- There is no set age, but it’s advisable to start early, incorporating a calcium-rich diet and regular exercise into your lifestyle.
- Are men at risk of osteoporosis?
- Yes, although women are more prone to osteoporosis, men can also develop this condition, especially in later years.
- Can osteoporosis be reversed once diagnosed?
- While it can’t be entirely reversed, early intervention and treatment can slow down its progression.
- Are there any natural remedies to boost bone health?
- Consuming foods rich in calcium and vitamin D and engaging in weight-bearing exercises are natural ways to improve bone health.
- Is osteoporosis hereditary?
- While it can run in families, it’s not entirely hereditary. Lifestyle choices also play a significant role in its development.






 Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
