Exploring the Potential of Nanotechnology in Medicine
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Nanotechnology?
- Nanotechnology’s Impact on Medicine
- Targeted Drug Delivery
- Imaging and Diagnostics
- Regenerative Medicine
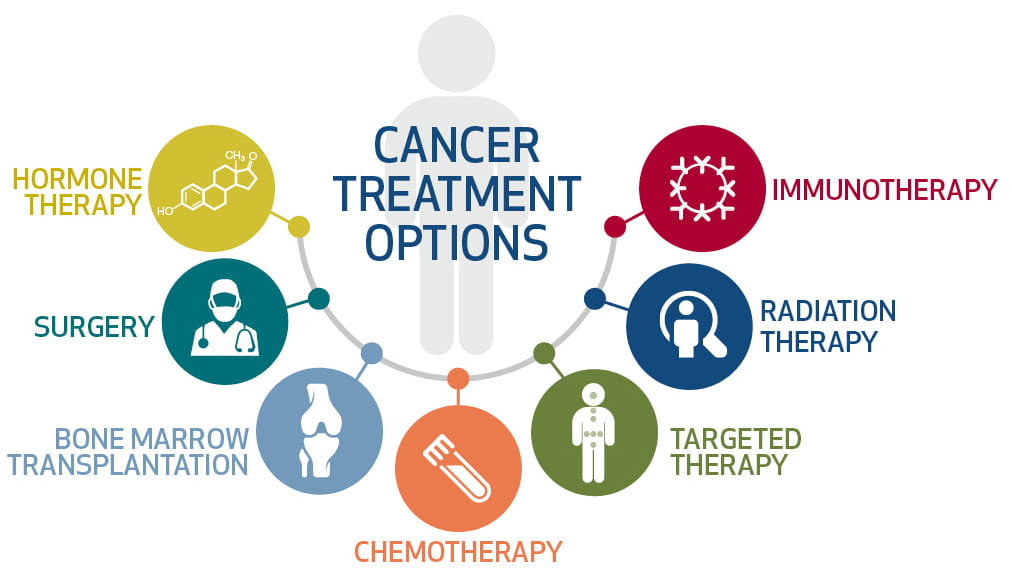
- Cancer Treatment
- Personalized Medicine
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations
- Safety Concerns
- Regulatory Issues
- Privacy and Data Security
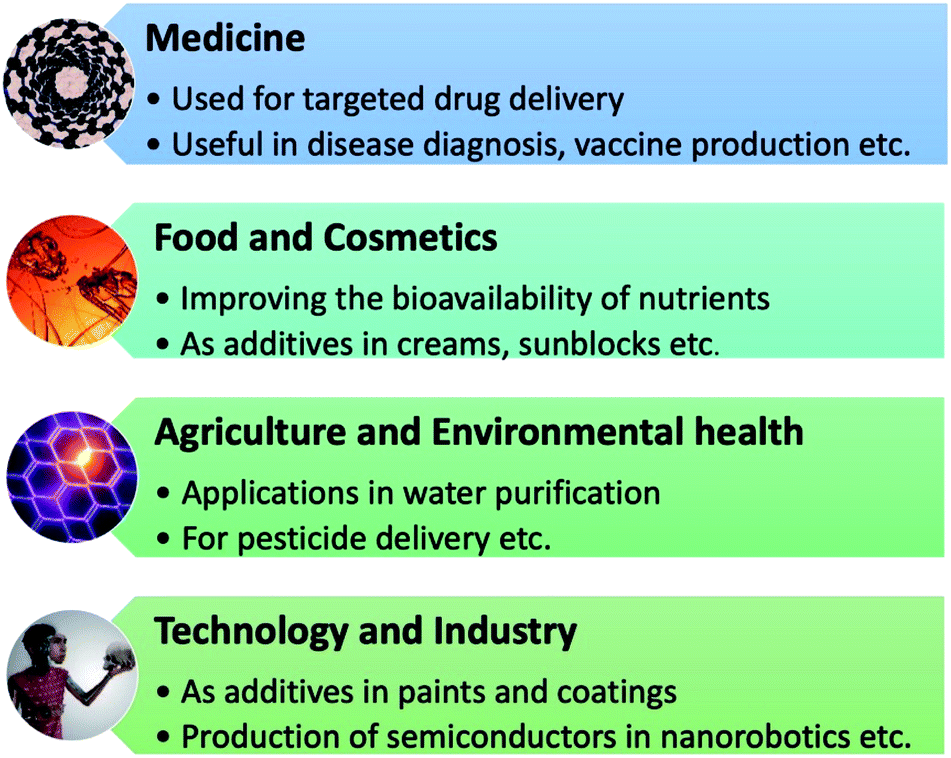
- Current Applications of Nanotechnology in Medicine
- Future Prospects and Advancements
- A Glimpse into Nanomedicine Research
- Integrating Nanotechnology with Traditional Medicine
- The Role of Nanorobotics in Healthcare
- Nanotechnology in Vaccines Development
- Nanotechnology and Neurological Disorders
- Nanomedicine and Global Health
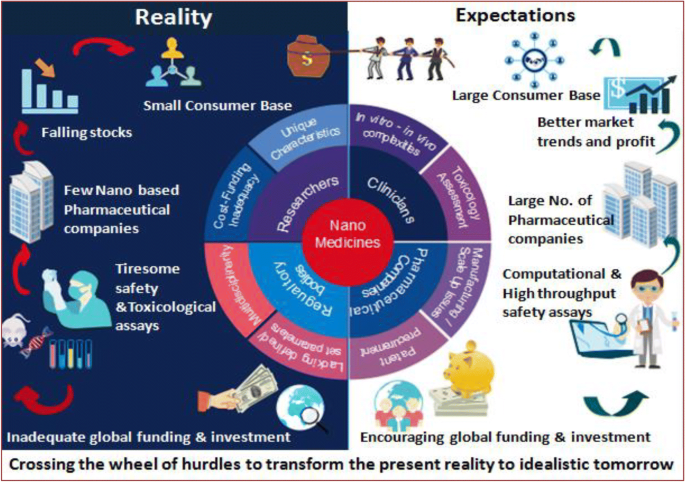
- The Economic Impact of Nanotechnology in Healthcare
- Environmental Implications of Nanomedicine
- Conclusion
Introduction
Nanotechnology, the manipulation of matter on an atomic and molecular scale, has emerged as a revolutionary field with profound applications in various industries. One of the most promising areas is its integration into the field of medicine. This article explores the vast potential of nanotechnology in transforming healthcare and revolutionizing medical treatments.
What is Nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology involves engineering and manipulating materials at the nanoscale, typically between 1 to 100 nanometers. At this level, the properties of materials exhibit unique characteristics that can be harnessed for specific purposes. In medicine, nanotechnology allows for targeted interactions with biological molecules, enabling precision in diagnosis and treatment.

Nanotechnology’s Impact on Medicine
1. Targeted Drug Delivery
Nanoparticles can be engineered to carry drugs directly to the affected cells or tissues, increasing drug efficacy and reducing side effects. This targeted drug delivery system holds great promise for treating chronic conditions and diseases.
2. Imaging and Diagnostics
Nanotechnology enhances medical imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, by providing better contrast and resolution. Additionally, nanosensors can detect disease biomarkers at an early stage, enabling timely and accurate diagnostics.

3. Regenerative Medicine

Nanomaterials facilitate tissue regeneration by creating scaffolds that promote cell growth and healing. This approach is particularly beneficial in treating injuries and degenerative diseases.
4. Cancer Treatment
Nanoparticles can deliver anti-cancer drugs directly to tumor cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues and improving treatment outcomes. Nanotechnology also plays a vital role in photothermal therapy and gene therapy for cancer treatment.
5. Personalized Medicine
![PDF] Personalized Medicine – A Valuable Tool in Healthcare Management | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/da85665482e309a9be9844f70c656cc97288acf1/3-Figure2-1.png)
With nanotechnology, it becomes feasible to tailor medical treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup and specific medical conditions. This personalized approach enhances treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its immense potential, nanotechnology in medicine faces challenges that must be addressed:
1. Safety Concerns
The potential toxicity of nanoparticles raises safety concerns that need rigorous evaluation to ensure patient safety.
2. Regulatory Issues
The fast-paced advancements in nanomedicine require clear regulatory guidelines to govern research, development, and commercialization.
3. Privacy and Data Security
The use of nanosensors and other technologies for data collection in medical applications raises privacy and data security concerns.
Current Applications of Nanotechnology in Medicine
Nanotechnology is already making a significant impact in medicine, with various products and treatments in use today. These include nanoscale drug formulations, nano-based medical devices, and nanosensors for disease detection.
Future Prospects and Advancements
The potential of nanotechnology in medicine is vast, and ongoing research promises exciting advancements in areas like nanorobotics, smart drug delivery systems, and nanovaccines.
A Glimpse into Nanomedicine Research
Researchers worldwide are exploring novel nanomedicine applications, including nano-based therapies for neurodegenerative diseases and nanomaterials for wound healing.
Integrating Nanotechnology with Traditional Medicine

Nanotechnology can complement traditional medical practices, augmenting treatment options and improving patient outcomes.
The Role of Nanorobotics in Healthcare

Nanorobots hold promise as future medical tools, capable of performing precise tasks within the human body, such as targeted drug delivery and microsurgery.
Nanotechnology in Vaccines Development

Nanotechnology has the potential to revolutionize vaccine development, enabling more effective and adaptable immunization strategies.
read more about The Importance of Vaccination
Nanotechnology and Neurological Disorders
The application of nanotechnology in understanding and treating neurological disorders offers new possibilities for improving the lives of affected individuals.
Nanomedicine and Global Health
Nanotechnology’s scalability and cost-effectiveness can enhance healthcare access and affordability in resource-limited regions.
The Economic Impact of Nanotechnology in Healthcare
Nanomedicine’s economic implications are far-reaching, influencing drug development, medical device manufacturing, and healthcare costs.
Environmental Implications of Nanomedicine
Understanding the environmental impact of nanomedicine is crucial to ensure sustainable and responsible development.
Conclusion
The integration of nanotechnology in medicine has opened up new horizons for the future of healthcare. Its potential to revolutionize drug delivery, diagnostics, regenerative medicine, and cancer treatment holds great promise. However, addressing safety concerns and ethical considerations is essential for responsible implementation. As research progresses, nanomedicine will continue to reshape the healthcare landscape, offering personalized and effective solutions to various medical challenges.
FAQs
Q1: What is nanotechnology?
Q2: How does nanotechnology benefit medicine?
Q3: Are there any safety concerns associated with nanomedicine?
Q4: What are the current applications of nanotechnology in medicine?
Q5: How does nanotechnology impact global health?






 Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine

1 Comment