Demystifying Antibiotics: How They Work and When to Use Them
Outline
Introduction
-
- Definition of antibiotics
- Importance of understanding antibiotics
-
How Antibiotics Work
- Mechanism of action
- Types of antibiotics
- Bacterial targets
-
Proper Use of Antibiotics
- Prescribing antibiotics
- Antibiotic resistance
- Importance of completing the full course
-
Common Misconceptions about Antibiotics
- Antibiotics for viral infections
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics
-
Side Effects and Precautions
- Common side effects
- Allergic reactions
- Antibiotics and pregnancy
-
Alternatives to Antibiotics
- Natural remedies
- Prevention strategies
-
Conclusion
-
FAQs
Demystifying Antibiotics: How They Work and When to Use Them
Antibiotics are powerful medications that have revolutionized the field of medicine by effectively treating bacterial infections. Understanding how antibiotics work and when to use them is crucial to ensure their appropriate and effective usage. In this article, we will delve into the world of antibiotics, exploring their mechanism of action, proper usage, common misconceptions, side effects, and alternatives.
read more about Antibiotics: Combatting Infections with 4 Simple Methods
How Antibiotics Work
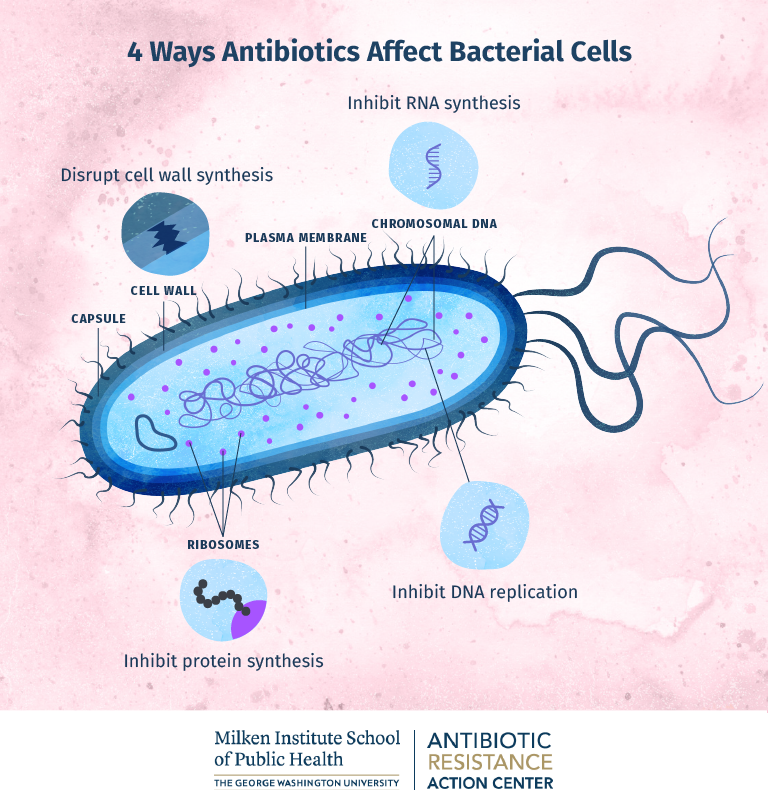
Antibiotics function by specifically targeting bacteria, either by directly killing them or by impeding their growth and reproduction. They accomplish this through various mechanisms of action, such as disrupting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls or interfering with essential metabolic processes. Different types of antibiotics exist, including penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones, each with its own specific target and mode of action. Understanding the specific bacterial target of an antibiotic is essential in selecting the most effective treatment.
Proper Use of Antibiotics

Prescribing antibiotics requires careful consideration to ensure their appropriate use. Antibiotic resistance has become a significant global health concern, fueled by the overuse and misuse of these medications. Healthcare professionals must adhere to evidence-based guidelines when prescribing antibiotics, taking into account factors such as the type of infection, the susceptibility of bacteria, and the patient’s medical history. It is crucial for patients to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if their symptoms improve, to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance and potential treatment failure.
Common Misconceptions about Antibiotics

One common misconception is the belief that antibiotics can effectively treat viral infections, such as the common cold or flu. However, antibiotics are only effective against bacteria and have no impact on viruses. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics in viral infections not only fail to provide any benefits but also contribute to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. It is essential to educate the public about the appropriate use of antibiotics to combat this issue.
Side Effects and Precautions

While antibiotics are generally safe and well-tolerated, they can have side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal pain. Allergic reactions to antibiotics can also occur, ranging from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis. Pregnant women need to exercise caution when taking antibiotics, as some may pose risks to the developing fetus. It is crucial to discuss any concerns or potential risks with a healthcare professional.
Alternatives to Antibiotics
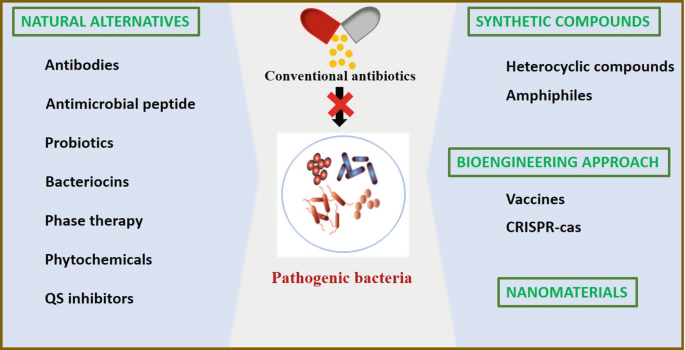
In certain cases, antibiotics may not be the only option for treating infections. Natural remedies, such as herbal supplements or essential oils, can sometimes provide relief for mild bacterial infections. However, it is important to note that natural remedies are not a substitute for antibiotics in severe or life-threatening infections. Prevention strategies, such as good hygiene practices and vaccinations, play a vital role in reducing the need for antibiotics and preventing the spread of bacterial infections.
Conclusion
Antibiotics are powerful tools in combating bacterial infections. Understanding their mechanism of action, appropriate usage, and potential side effects is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. By using antibiotics judiciously and educating ourselves about their proper use, we can contribute to the fight against antibiotic resistance and ensure these medications remain effective for future generations.
FAQs
Q: What are the typical adverse effects associated with antibiotics
A: Common side effects of antibiotics may include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal pain. It is vital to seek advice from a medical professional if any side effects arise
Q: Can antibiotics treat viral infections?
A: No, antibiotics are specifically designed to combat bacterial infections and do not have any impact on viral infections like the common cold or flu.
Q: How long should I take antibiotics?
A: It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your healthcare professional, even if your symptoms improve. Failure to do so may contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance.
Q: Are there any natural alternatives to antibiotics?
A: Some natural remedies, such as herbal supplements or essential oils, may provide relief for mild bacterial infections. However, severe or life-threatening infections require appropriate medical treatment with antibiotics.
Q: Is it safe to take antibiotics during pregnancy?
A: The safety of antibiotics during pregnancy depends on the specific medication. It is essential to discuss any concerns or potential risks with your healthcare professional to ensure the best course of action for you and your baby.




 Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine

1 Comment