Vaccine Boosters: The Key to Long-Lasting Protection

In a world grappling with evolving viruses and emerging variants, the quest for effective protection against infectious diseases has taken center stage. As we navigate the landscape of vaccination, one term has gained prominence: “booster vaccines.” These crucial additional doses are poised to be the key to long-lasting immunity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of booster vaccines, exploring their significance, how they work, and why they are essential in safeguarding our health.
Understanding the Need for Booster Vaccines

What Are Booster Vaccines?
Booster vaccines are supplementary doses of a vaccine that are administered after the initial vaccination series. They serve as a reinforcement of the immune response, ensuring that your body maintains a robust defense against specific pathogens.
The Waning Immunity Dilemma
Over time, the immunity provided by some vaccines can gradually decrease. This phenomenon, known as waning immunity, leaves individuals vulnerable to infection, especially when confronted with new variants of the virus.
Addressing Emerging Variants
Emerging variants of viruses, such as the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, have posed significant challenges to existing vaccines. Booster vaccines can be tailored to combat these new strains, providing enhanced protection.
How Booster Vaccines Work
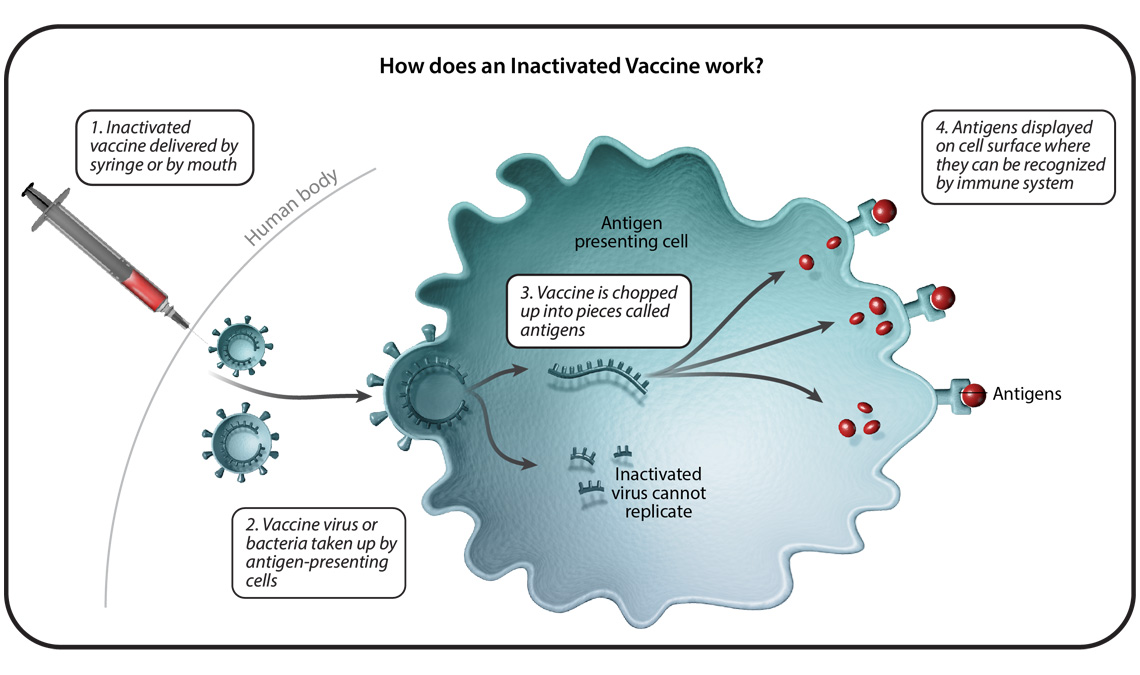
Boosting Immune Memory
Booster vaccines rekindle your immune memory. They remind your body how to recognize and fight the pathogen, essentially giving your immune system a refresher course in combating the virus.
Antibodies and T-Cells
These supplementary doses stimulate the production of antibodies and activate T-cells, both of which play pivotal roles in neutralizing the virus and preventing severe illness.
The Significance of Booster Vaccines
Prolonged Protection
By strengthening the immune response, booster vaccines extend the duration of protection against diseases, reducing the need for frequent revaccination.
Herd Immunity
Achieving herd immunity, where a significant portion of the population is immune to a disease, is a critical public health goal. Booster vaccines contribute to this by bolstering overall immunity levels.
Pandemic Preparedness
In the face of pandemics, booster vaccines are vital tools in our arsenal. They allow us to adapt swiftly to new threats and maintain our defenses against evolving viruses.
Dispelling Myths and Concerns
Safety and Efficacy

Booster vaccines undergo rigorous testing to ensure safety and effectiveness. They are subject to the same stringent standards as initial vaccines.
Impact on Global Vaccine Equity

While booster doses are essential in high-risk populations and regions, efforts must continue to ensure that vaccines are accessible to all, addressing global vaccine equity concerns.
Conclusion
Booster vaccines are not just a medical innovation; they represent our resilience in the face of ever-changing pathogens. They are the guardians of our long-lasting protection, helping us navigate the complex landscape of infectious diseases with confidence. As we look ahead, it’s clear that booster vaccines will remain an essential part of our public health strategy.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Are booster vaccines safe?
- Yes, booster vaccines undergo rigorous testing to ensure safety and efficacy, just like initial vaccines.
- How often do I need a booster vaccine?
- The frequency of booster doses depends on the specific vaccine and the pathogen it targets. Consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
- Do booster vaccines protect against new variants of the virus?
- Booster vaccines can be adapted to target emerging variants, providing enhanced protection.
- Do booster vaccines have side effects?
- Like any vaccine, booster doses may have side effects, but they are generally mild and temporary, such as soreness at the injection site or mild fatigue.
- Why is global vaccine equity important in the context of booster vaccines?
- Global vaccine equity ensures that everyone, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status, has access to vaccines, reducing the global spread of infectious diseases and the emergence of new variants.





 Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine
Viesearch - The Human-curated Search Engine

4 Comments